Note: Text revised and updated June 2024
WHAT IS SEO?
Search engine optimisation (SEO) is the process of getting a web page to show higher up in organic search results – that is, the results which appear naturally in response to a search query rather than those shown because they’ve been paid for.
Put simply, the aim of SEO is to get your pages to appear on the first page of Google (ideally in the number one spot) without having to pay for them to be there.
Why the first page?
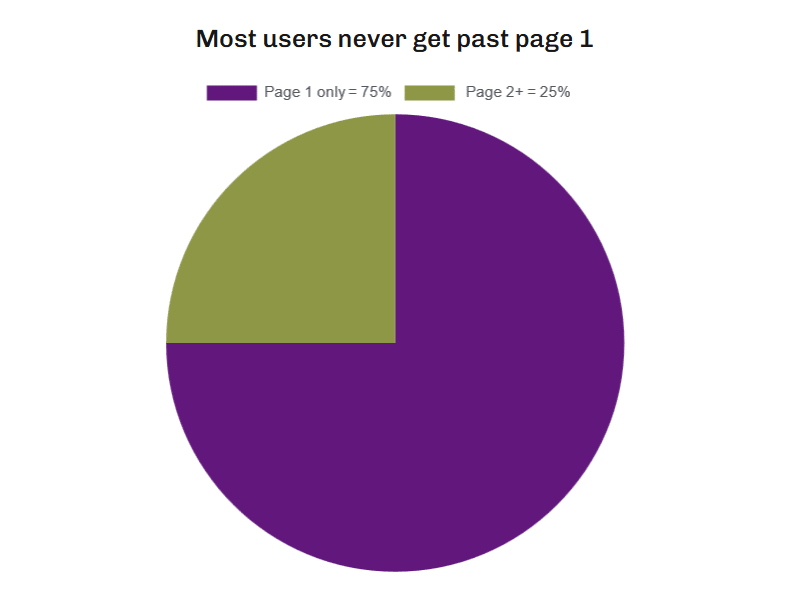
An estimated 75% of users never get beyond page one of their search results, so appearing on the first page significantly increases your chances of being seen.
(Note that the 75% figure is widely quoted, but with very little reference to the source. In HubSpot’s 100 Awesome Marketing Stats, Charts and Graphs credit is given to research from 2010 by NetMarketShare – but the data is no longer available. More recent information on how many people never get beyond the first page of search results doesn’t seem to have been published. Other sources suggest the figure could be as high as 90% – but again with no hard evidence.)
Why Google?
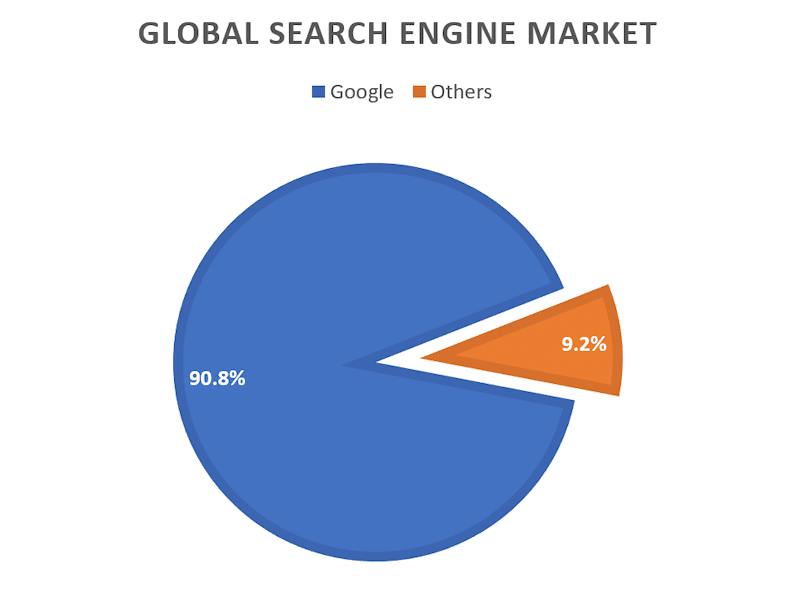
Google dominates the search engine market.
In May 2024, according to StatCounter, Google had 90.8% of the global search market.
For the UK, the figure was slightly higher at 94.28%; for the US it was 87.14%.
Bing was the second most used search tool in both countries, with 3.53% and 7.81% of the market respectively.
So, with Google accounting for the vast majority of searches and three quarters of people never venturing beyond page one, it makes sense for SEO to target the first page of Google.
Why number one on Google?
It also makes sense to get as high up the page as possible. Research by Sistrix shows that over a quarter (28.5%) of clicks on the results page go to the first result shown, with the second result getting 15.7% and the third 11%.
Between them, those first three results therefore account for more than half (55.2%) of all clicks – while on average, the last result (number 10) is clicked by just 2.5% of people searching.

For more, see Why (almost) everything you knew about Google CTR is no longer valid.
Whilst alarming, these figures should not be surprising. After all, Google’s mission is to present its users with the ideal result first time – so they should never need to scroll past the top few search results (see 10 Useful Findings About How People View Websites).
Why is SEO important?
The importance of search engine optimisation (SEO) lies in its ability to get websites noticed by people who are searching online for the products, services, information etc being offered.
Given that there’s little point in having a website that’s never seen by potential customers, SEO offers businesses and other organisations the potential to get relevant web pages in front of their target audience.
Research shows that only a small proportion of people searching for something click on paid advertisements.
According to FirstPageSage, the clickthrough rate (CTR) for an advert in number one position is just 2.1%, while the CTR for a first placed organic search result is 39.8% (see Clickthrough Rates (CTR) for Organic vs Paid Search).
WHAT IS A SEARCH ENGINE?
A search engine is a computer program used to find information on the internet, usually in response to one or more keywords being typed in but also, increasingly, to voice commands.
Google is by far the best known and most widely used search engine, with over 90% of market share (see this search engine data from StatCounter).
The aim of Google and other search engines, such as Bing, Yahoo and Duck Duck Go, is to present users with the most relevant results for their search, in the form of web pages, images, videos and other materials.
For more information, see Techopedia’s definition of search engine.

HOW DO SEARCH ENGINES WORK?
As explained below, search engines work by performing three distinct actions: crawling, indexing and ranking:
Stage 1 – Crawling
Crawlers (aka ‘spiders’, ‘robots’, ‘bots’) find and analyse information on websites.
Starting from a page it already knows about, a crawler follows links not only to pages on the same site (internal links) but also to pages on other sites (external links).
Following internal links enables the spider to discover both new content (e.g. a new blog post) and changes to existing content (e.g. updated contact details) on the original site, while tracing external links helps assess its relative importance (such as how many sites are linked to and link back to it, and how important they are).
By following links, analysing content and seeing how various pages and sites are connected, the crawler builds up a picture of what websites and their individual pages are about – and how relevant they might be to a search query.
To assess that relevance, search engines look at keywords, including how frequently they appear, whether they appear in headings and, if they do, how well those headings match the content of the page and site.
Note that it’s not all about keywords: when crawling a site, search engines also take other factors into consideration, such as how fast a page loads and how easy it is for users to navigate a site.
Stage 2 – Indexing
Once a website has been crawled, the search engine decides if the site’s content is worth indexing. If it is, the content is added to the engine’s database and becomes available for display in response to keyword searches.
With the exception of ‘stop’ words every word on a page that Google indexes is added to the database and Google’s index now contains hundreds of billions of web pages.
(See How Google Search organises information; for information about stop words, see this CSEO article: SEO Stop Words: The Definitive Guide.)
Because Google and other search engines are in business to present their users with the most relevant information, not all content is indexed.
To guarantee being indexed, a site should offer content that is both unique and valuable. Duplicating material available elsewhere or offering poor quality, spam-laden content will hurt a site’s chances of being indexed – as will anything that stops search engines crawling a site.
Stage 3 – Ranking
The final stage is for a website to be ranked.
Just as some websites are of such poor quality that they are not indexed, some web pages are considered to be more appropriate to a particular query and are therefore displayed nearer the top of the search results.
Deciding which of the pages that it’s indexed should be displayed in response to a search is a task for a search engine’s algorithms.
It’s generally accepted that Google uses over 200 factors to assess how well a page ranks. They include whether and where keywords are found, whether a page loads quickly and is mobile friendly, and whether a web page and the site of which it is part can be considered a reputable source of information for a particular subject.
In response to a search, the most relevant organic results (not paid advertisements) are ranked and then displayed on a series of search engine results pages (SERPs). For more information, see the Ahrefs page How Search Engines Work.

HOW DOES SEO WORK?
The aim of SEO is to persuade Google and other search tools to display your website’s pages as high up the list of search results as possible.
To achieve that aim, the process of search engine optimisation focuses on a number of objectives related to both internal website issues and external factors – known in the jargon as on-page and off-page optimisation respectively.
Through a variety of activities, including monitoring the performance of your site’s pages, amending keywords, adding new content and promoting your site via social media and other channels, SEO works to convince Google that your web pages are the ones it should be showing when people search for relevant keywords.
It’s worth bearing in mind that, when Google is analysing your website, one of its most important considerations is trust; that is, the extent to which your pages are accurate, honest, safe, and reliable.
Page quality – and hence your ranking in relation to similar pages from other providers – is assessed using what Google terms E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trust.
This was previously EAT: Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness; for more information see:
Google: Our latest update to the quality rater guidelines: E-A-T gets an extra E for Experience
MOZ: Google E-E-A-T
Search Engine Journal: Google E-E-A-T: What Is It & How To Demonstrate It For SEO
What is on-page SEO?
The term on-page SEO, or on-page optimisation, refers to addressing issues on your website, in order to maximise the potential for pages to be found, indexed and ranked by search engines.
When looking at your website from an SEO perspective, it’s worth remembering that search engine crawlers only see text: there are no vibrant colours and stunning images, just words. Unless you provide content that a crawler can read, then however beautiful your site and its pages are, they’re likely to remain undiscovered by potential customers.
Activities associated with on-page SEO therefore include creating high quality, useful content that search engines can access, and making sure that keywords appear in relevant places, such as title tags, meta descriptions and image alt tags.
On-page optimisation also covers things like creating good URLs for pages and blog posts (and ensuring that words in URLs are separated by hyphens, not underscores or some other character that crawlers struggle to interpret), reducing the size of image files, and making sure that links (and the pages they point to) are accessible to search engines.
It’s also important to make sure that your website is responsive, so that people seeing it on mobile devices find it easy to view, navigate and read, so this is another area that on-page SEO addresses.
What is off-page SEO?
In contrast to on-page SEO, the aim of off-page optimisation is to increase awareness of your site and its contents by engaging in activities beyond its borders.
It is essentially a means of bringing your pages to the attention of other people and websites through activities such as social media marketing and posting in relevant online forums.
If you’re dubious about the role of social media in search engine optimisation, here are some articles that might help change your mind:
Search Engine Journal article: How Social Media Helps SEO,
Coalition Technologies: How Posting on Social Media Can Help Your SEO in 2024
OptinMOnster: Social Media SEO: How To Incorporate Social Media Into SEO Strategy
Conductor: The Impact of Social Media on Page Rank
SEO.com: Does Social Media Help SEO? 6 Benefits of Social on SEO
Another objective of off-page SEO is to get other websites to link to your pages, through a process called link building. Known as ‘backlinks’, these are an important ranking factor for Google; the more backlinks you have from reputable sources, the more significant your site is considered to be.
Guest blogging is also cited as a good way of attracting attention to your site. If you can write blog posts for other quality sites in a related sector, then search engines take that as a sign that you have some expertise in the subject and they can reward your efforts by pushing you higher up the rankings.

CAN I DO SEO MYSELF?
If you understand how your website is structured, can add and amend its contents, know where and how to use headings and to add metadata, can write reasonably well, and have plenty of time and patience, then ‘yes’ you can do search engine optimisation yourself.
You might also need to improve the speed at which your pages load by, for example, making sure you have a quality hosting package and compressing your images.
And don’t forget to ensure a good user experience for people viewing your site on mobile devices.
If you’re happy you can manage all of this, then go for it. Just be aware that SEO is an ongoing process, which can take anything from weeks to years to bear fruit – hence the need to be patient.
Where do I start with SEO?
A good place to start your SEO journey is to do some reading around the subject. My own reading list comprises a few books and lots of online sources, including:
Books
Search Engine Optimization All-in-One For Dummies
SEO 2022: Learn Search Engine Optimization With Smart Internet Marketing Strategies
Online
Google: Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Starter Guide
Hubspot: How to Create an SEO Strategy for 2024
Mangools: The Complete SEO Guide for Beginners
Revenue River: How to Start an SEO Campaign
Yoast: SEO tutorial for beginners: How to start with SEO?
Five ideas for doing SEO yourself …
It’s easy to be overwhelmed by the amount of information available. If you’d rather just focus on a few steps to get you started with SEO, here are five actions you can take:
1 – Build a keyword list
Think about how your website visitors might search for your products, services etc and build a list of 10-20 keywords that you think they’ll use.
Bear in mind that in the context of SEO, the term ‘keyword’ refers both to single words and to phrases.
You should find it easier to rank higher for what are known as ‘long-tail’ keywords: phrases of three or more words that have relatively low search volumes.
That’s because these longer, more specific search terms have less competition than ‘short tail’ options, which attract more searches.
In my own case, for example, on 1 January 2023 I ranked number one on Google for the long-tail phrase ‘wordpress website designer north wales’ (and in June 2024 was still high, at number three), but I didn’t even make the first 10 search results pages (SERPs) for the more general keyword ‘wordpress designer’.
Although long-tail keywords attract less attention individually, if you can rank highly for enough of them, then collectively they can generate sufficient traffic to make the effort worthwhile.
For more information see:
Keyword generators
Long-tail and short-tail keywords
Ahrefs: Long-tail Keywords: What They Are and How to Get Search Traffic From Them
Ahrefs: Short-tail keywords
Backlinko: Long Tail Keywords
HubSpot: Top 15 Tools For Finding Long-Tail Keywords in 2023
2 – Search Google yourself
Using your keyword list, do your own Google search for each one and see where your pages appear in the SERPs (it’s probably not worth looking further than the first 10 pages).
SEO is about improving your keyword ranking, so note the date of the search and where each term appears in the SERPs (page number and position), so that you have something to act as a baseline to chart your progress.
3 – Set your SEO goals
Once you’ve got an idea of how your keywords are ranking, set yourself some goals.
You might want to choose a few key phrases and set the target of getting them to page one within a certain period.
Or you might want to rank higher than a competitor, or generate a minimum number of visits to your website.
Whatever goal you choose, be realistic. It’s better to achieve smaller gains and remain positive than to set yourself an unrealistic target and give up. And remember – success with SEO can take time.
4 – Install an SEO plugin
If, like me, you’ve built your website using WordPress, then think about installing an SEO plugin.
A plugin such as Yoast, Rank Math or The SEO Framework (which I use) can help enormously in improving your SEO results.
There are lots to choose from; some are free, others cost money; some can be relatively easy to set up, other more complex.
You can always uninstall something that you don’t like, but before committing yourself try Googling ‘wordpress seo plugin’ and read some of the articles which compare, contrast and recommend plugins to learn more and find one that suits you.
5 – Write good content
The key to getting your page to rank highly on Google is good content. Google wants to know why it should display your page above those of your competitors.
Publishing material that is both unique and valuable will answer that question and ensure that your pages are indexed, their contents added to the engine’s database, and that they are displayed on SERPs in response to keyword searches.
Focus on building content rich pages for each topic your site covers, make sure your site includes a blog which is added to at least once a month, and share your content on social media.
For more on the importance of blogging for SEO, see:
Ahrefs: Blog SEO: The Complete Guide
Backlinko: Blog SEO
HubSpot: Blog SEO: How to Search Engine Optimize Your Blog Content
WPBeginner: 11 Tips to Optimize Your Blog Posts for SEO Like a Pro
12 TIPS FOR BETTER SEO
Finally, here are 12 bonus tips which can help make your website and its pages more appealing to Google and other search engines:
1) Give all your pages unique titles.
2) Make sure that the content of each page is different.
3) Make sure your content is readable. Avoid large blocks of text, use colours that make your words easy to see on the screen, and use UPPER CASE sparingly.
4) Add new content regularly and give old content a makeover.
5) Emphasise important pages by using internal links.
6) Use relevant keywords in page titles, headings, alt image tags and other places, but make sure that texts read naturally and aren’t just full of keywords.
7) Write for people, not search engines, and try to use simple language.
8) Demonstrate your expertise by writing – and maintaining – a blog.
9) Answer questions that your visitors might have via a FAQ section.
10) Optimise images to reduce page loading time.
11) Make sure your site has an SSL certificate.
12) Use social media to highlight and share your content.
SUMMARY
The aim of SEO is to get your pages to appear high in the list of results when people search for terms relevant to your business, without using paid advertisements.
SEO falls into two main categories: on-page optimisation and off-page optimisation.
You can do search engine optimisation yourself and this article suggests five actions you can take to get started on your SEO journey, plus 12 tips for making your pages more appealing to Google.
Just remember that, whether you choose the DIY approach or pay someone to do it for you, SEO is an ongoing process, not a quick fix.
* This article is also available as a PDF file: A guide to search engine optimisation and there is a series of pages on my website on the topic, which starts with Introduction to SEO.